NEMA stepper motor sizes chart and selection guide
-
Automation
-
Health & wellness
-
Life environment
-
Automotive
-
Space
26 Nov. 2025
When selecting a stepper motor, you may encounter the term “NEMA size.” A NEMA size refers only to mounting dimensions and not motor performance. It does not define torque or electrical characteristics, so you cannot choose a motor based on the NEMA size alone. This article explains NEMA size definitions, provides a NEMA stepper motor chart and highlights other critical factors for selecting the right stepper motor.
Definition of “NEMA size” in NEMA motor standards
What is NEMA?
NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) is a U.S. standards organization. For stepper motors, specifications are defined in NEMA ICS 16-2001, which standardizes flange dimensions, mounting hole positions, etc. This ensures mechanical compatibility across different manufacturers.
NEMA size specifies physical mounting dimensions only, not performance
Designations such as NEMA 17 or NEMA 23 correspond to the approximate width and height of the square mounting flange in inches. For example:
- NEMA 17: Approx. 1.7 inches (42 mm)
- NEMA 23: Approx. 2.3 inches (56 mm)
NEMA ICS 16-2001 primarily defines the following dimensions:
- Width and height of the square type mounting flange (or outside diameter of the round type flange)
- Diameter and position of the holes in the mounting flange
- Diameter and depth of the pilot
The NEMA sizes only specify physical dimensions on the mounting and shaft, and do not define torque, speed, or electrical ratings. Stepper motors of the same NEMA size can differ greatly in length, winding, and performance.
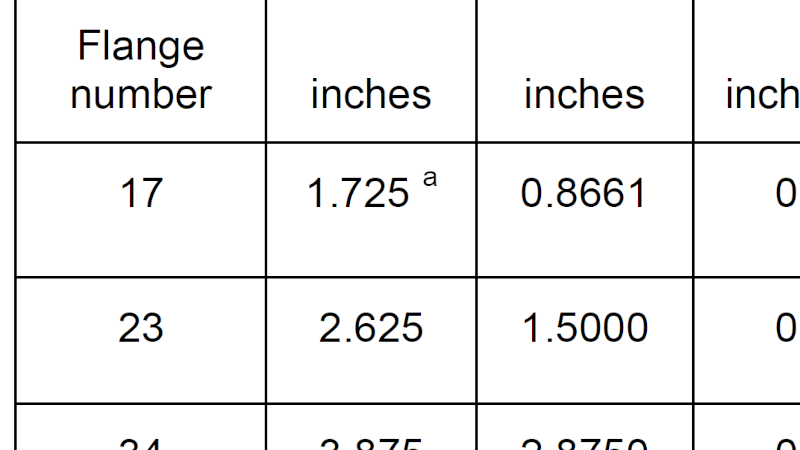
Dimension values defined by NEMA and size chart
The following table shows examples of dimensions specified for each NEMA size in inches. These have been excerpted and formatted from “Table 2 — Shaft number designation” and “Table 4 — Dimensions for mounting flanges for inch dimension motors” in NEMA ICS 16-2001.
| NEMA size |
Width and height of square flange (reference) BD Inches |
Max. outside diameter of round flange P Inches |
Nominal pilot diameter N Inches |
Min. and max. pilot depth T Inches |
Diameter of free holes for square flange (Nominal and tolerance) S Inches |
Nominal shaft diameter D Inches |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 17 | 1.7 | 2.36 | 0.8661 | 0.03-0.09 | 0.150±0.010 | 0.1969 |
| 23 | 2.3 | 3.21 | 1.5000 | 0.06-0.13 | 0.205±0.010 | 0.2500 |
| 34 | 3.4 | 3.58 | 2.8750 | 0.06-0.13 | 0.220±0.010 | 0.3750 |
| 42 | 4.2 | 6.19 | 2.1875 | 0.06-0.13 | 0.280±0.010 | 0.6250 |
NEMA standard: “Motion/Position Control Motors, Controls and Feedback Devices”
 Example of an external view drawing of the ASPINA stepper motor STA-42D series. The elements enclosed in the square are specified by the NEMA standard.
Example of an external view drawing of the ASPINA stepper motor STA-42D series. The elements enclosed in the square are specified by the NEMA standard.
The diameter of the round flange and the position of the mounting holes are strictly defined by the NEMA standard. For square flanges, the width and height are treated as a reference value in the standard. However, as a customary practice, ASPINA sets those of the square flange of our stepper motors to match the NEMA size number.
ASPINA stepper motors by NEMA size and typical applications
At ASPINA, we provide clear information for each model to make it easier for customers who select stepper motors by size. The following table lists our stepper motor models along with their NEMA sizes and typical applications.
| Application | NEMA11 | NEMA14 | NEMA16 | NEMA17 | NEMA17 | NEMA23 | NEMA24 | NEMA34 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SST28D | SST35D | SST36C | SST42C | STA-42D | STA-56D | SST60D | SST86D | |
| Nozzle and ink head in 3D printers | Yes | |||||||
| Paper feeder and sorter (e.g., banknotes, copy paper) | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Belt conveyor roller drive | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Tool, nozzle and table in machine tools | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||
| Light and projector in stage/stadium lighting | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Syringe pump | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||
| Arm mechanism in robotic arms, etc. | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Louver in air conditioners | Yes | Yes | ||||||
| Solar panel in space satellites | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Valve actuator | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | ||||
| Surveillance camera | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Aperture such as antennas on space satellites | Yes | Yes | Yes | |||||
| Sample stage in SMEs or analyzers | Yes | Yes | Yes |
The information in this table is current as of the publication date of this article.
Beyond the chart: What NEMA does not tell you
NEMA size specifies only certain physical dimensions of a stepper motor. The following specifications are not defined in NEMA sizes, yet they are critical when selecting the right motor for your application:
- Torque and speed
- Drive method
- Rated current and voltage
- Shaft length
- Step angle (e.g., 1.8°, 0.9°)
- Special environmental conditions (such as temperature)
- Presence of a gear mounted on the shaft
- Connector shape and position
How to choose the right stepper motor for your project
Check the mounting dimensions
Determine which NEMA size corresponds to the mounting interface on your equipment. Then, select a motor from the manufacturer’s lineup that can deliver the required torque within that size. However, if there is insufficient axial space, you may need to choose a stepper motor with a larger NEMA size to achieve the necessary torque.
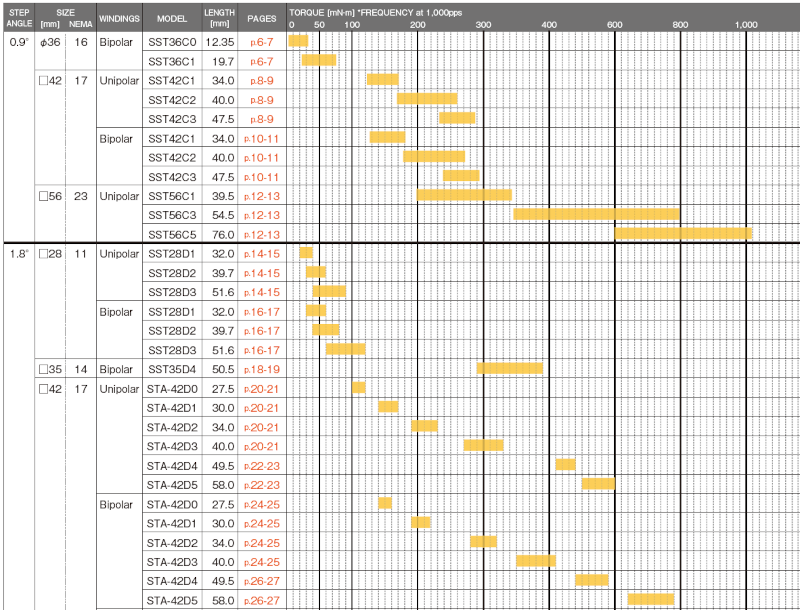 Example of torque ranges (pulse frequency: 1000pps) by step angle, NEMA size, winding type, and axial length for ASPINA stepper motors
Example of torque ranges (pulse frequency: 1000pps) by step angle, NEMA size, winding type, and axial length for ASPINA stepper motors
Understand torque requirements
Calculate the torque needed for your application and check its relationship to motor size. In addition to NEMA size, factors such as drive method and the motor’s axial length are important for identifying the right stepper motor.
Consider drive conditions
Review the relationship between drive method and current. The driver’s control method determines the winding configuration, which in turn affects torque, circuit ratings, and the current capacity of your equipment. These considerations help define the rated current.
Review other specifications
Shaft length, the necessity of a gear mounted on the shaft, connector type and position, which may affect mounting, as well as environmental conditions such as temperature are also important considerations.
Overcoming your problems with stepper motors
ASPINA supplies not only standalone stepper motors, but also system products that incorporate drive and control systems as well as mechanical design. These are backed by comprehensive support that extends from prototyping to commercial production and after-sales service.
ASPINA can offer solutions that are tailored to suit the functions and performance demanded by a diverse range of industries, applications, and customer products, as well as your particular production arrangements.
ASPINA supports not only customers who already know their requirements or specifications, but also those who are facing problems at early stages of development.
Do you struggle with the following concerns?
Motor selection
- Don't have detailed specifications or design drawings yet, but need advice on motors?
- Don't have anyone in-house with expertise in motors and can't identify what sort of motor will work best for your new product?
Motor and associated component development
- Want to focus your resources on core technology, and outsource drive systems and motor development?
- Want to save the time and effort of redesigning existing mechanical components when replacing your motor?
Unique requirement
- Need a custom motor for your product, but been declined from your usual vendor?
- Can't find a motor that gives you the control you require, and about to give up hope?
Seeking answers to these problems? Contact ASPINA, we are here to help.
List of the same series columns
- What does a stepper motor do?
- What is a brushless DC motor? What is the difference between brushless motor and brushed motor?
- What is a DC motor? - DC motor types, how they work, and how to control them
- Applications for blower motor
- What is a blower motor?
- Features and applications of DC motors
- Advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors
- Is this brushless motor cheap or expensive? - What factors determine its price?
- What is a geared brushless DC motor?
- How does an electronic speed controller for a brushless DC motor work? And what should you consider when you choose the right one?
- Small brushless motors
- What are the disadvantages of brushless DC motors? And how can they be overcome?
- Advantages of brushless DC motors: How they differ from brushed DC motors
- What is an actuator?
- Do brushless DC motors require a drive circuit? – Controlling brushless DC motors
- What is a stepper motor?
- What is an electric motor?
- How are stepper motors controlled? - Speed control of stepper motors
- How are DC motors controlled? - Speed control of DC motors
- Brushless DC motor applications: examples that demonstrate their features
- Stepper motor applications: Examples that demonstrate their features
- Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
- What are the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
- What is a PSC motor
- What is a servo motor?
- What is a blower?
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others