Advantages of brushless DC motors: How they differ from brushed DC motors
-
Automation
-
Health & wellness
-
Life environment
-
Automotive
18 Aug. 2021
Brushless DC motors are controlled by electronics, which take the place of the brushes and commutator required by brushed DC motors. This article describes many advantages that brushless DC motors have over their brushed counterparts.
- Brushless DC motors do not have brushes
- Long life and low noise
- More reliable speed control than brushed DC motors
- Low electromagnetic noise
- Potential for energy saving
- Wide range of variations available to suit different product designs
- Incorporate the advantages of brushless DC motors to use in designs
Brushless DC motors do not have brushes
Brushed DC motors combine a rotating armature with stationary magnets (the stator), using brushes and commutator to supply current to the armature coil.
Brushless DC motors, in contrast, have a rotor, stator, rotation sensor, and control circuit. In place of the brushes and commutator, the current through the stator coil is controlled electronically by semiconductor switching.
Brushless DC motors can be divided into those with an outer rotor and those with an inner rotor.
- Outer-rotor motors
-
In these motors, a rotor containing permanent magnets rotates around the central stator. This configuration eliminates the need for the magnets to be kept small and facilitates equipment downsizing as it allows the outer rotor to be used as a fan driveshaft, for example.
- Inner-rotor motors
-
These motors have the opposite configuration to that of traditional brushed DC motors, with a cylindrical rotor containing magnets rotating inside coils that are arranged concentrically. This enables the rotor to have a small moment of inertia and facilitates miniaturization of the motor.
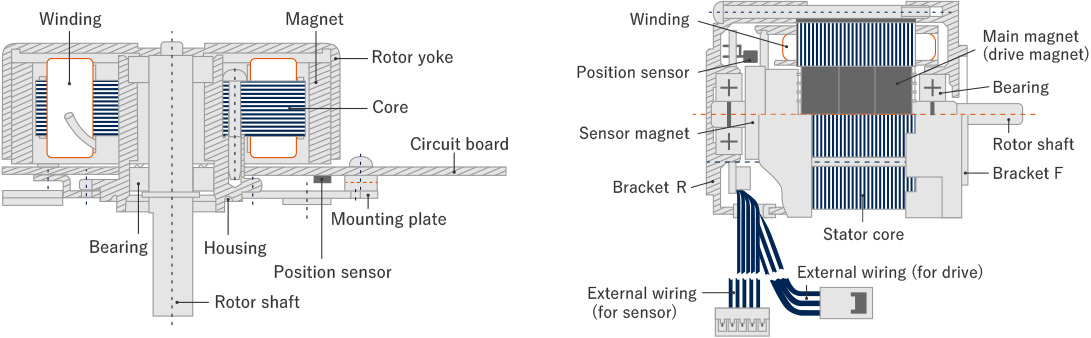 Brushless DC (BLDC) motors: Outer-rotor motor (left) and inner-rotor motor (right)
Brushless DC (BLDC) motors: Outer-rotor motor (left) and inner-rotor motor (right)
Long life and low noise
One problem with brushed DC motors is the wearing of the brushes and commutator, which are in constant contact. In some cases, abrasion of the brushes is also a source of dust or sparking.
No such wear occurs on brushless DC motors as they lack this mechanical contact. As the absence of abrasion dust or sludge prolongs the motor life, it helps reduce the frequency of maintenance for routine motor replacement. Choosing brushless DC motors for critical equipment extends its product life and avoids motor-related defects.
The characteristic scraping sound produced by brushed motors as the brushes rub against the commutator may be the result of resonance between parts or audible noise due to their rubbing against each other, sound produced by vibration or other movement in the rotor thrust direction, wind noise if the rotor has a built-in fan, or electromagnetic humming due to magnetic forces causing the stator core to vibrate.
More reliable speed control than brushed DC motors
As is the case for brushed DC motors, it is necessary to consider the moment of inertia of the motor shaft. Both the motor and power transfer (driveshaft) mechanisms have a moment of inertia, the size of which depends on weight, diameter, and length.
Appropriate control is needed to deal with the high startup torque that occurs when the motor starts to turn, which demands a higher current than when the motor is running at a steady speed. A certain amount of energy is also lost to heat and vibration whenever the shaft is turning.
In brushless DC motors, a Hall device (magnetic sensor) is used for feedback control and to determine the state of the motor. By adjusting the motor voltage, the motor speed can be kept constant despite changes in load. Precise speed control is possible with brushless DC motors.
Low electromagnetic noise
EMC considerations play an important role in part selection when you design a product.
Brushed DC motors tend to generate noise due to the significant sparking that occurs at each switching of contact between the brushes and commutator. Noise is a form of electromagnetic energy, just like other electrical signals. In the absence of appropriate control measures, it can interfere with other devices or electronic components, causing misoperation or degraded performance.
The motor current of brushless DC motors can be controlled electronically. As this tends to result in less electromagnetic noise, they are recognized as providing better conversion efficiency than brushed DC motors, with lower levels of energy loss and noise.
Potential for energy saving
The weight of individual parts is an important factor in reducing overall product weight. Because they do not require a brush assembly, the design of brushless DC motors is inherently more flexible, providing scope for reducing their size and weight. Furthermore, the smaller the parts of the motors, the less energy is needed to turn the motor.
Given that power consumption by electric motors is estimated to account for 40 to 50% of global electricity use, a higher conversion efficiency (meaning less electricity is required to deliver a given amount of rotational energy) also helps reduce the load on the environment.
The features of brushless DC motors, which include long life, ease of control, and low electromagnetic noise, are essential to ensuring reliable equipment control. They also contribute to extending the lives of appliances, personal computer peripheral equipment, and other such products.
The overall impact that products have on the environment is also reduced by using motors that do not contain any lead, hexavalent chromium, or other materials restricted by environmental standards such as RoHS.
Wide range of variations available to suit different product designs
In contrast to brushed DC motors that cannot function without brushes and commutators, brushless DC motors offer flexibility in the size and positioning of their control circuit. This means they can suit various spatial conditions of the target systems by using low profile rotors, positioning rotors around the systems, designing the motors in long and thin shape, etc.
Incorporate the advantages of brushless DC motors to use in designs
Whereas brushed DC motors run by means of their brushes and commutator, brushless DC motors use a switching element in the form of a semiconductor switch. The elimination of mechanical contact that comes with taking the brushes out of the motor also delivers numerous benefits. This article will help consider whether or not to use brushless DC motors.
Overcoming your problems with brushless DC motors
ASPINA supplies not only standalone brushless DC motors, but also system products that incorporate drive and control systems as well as mechanical design. These are backed by comprehensive support that extends from prototyping to commercial production and after-sales service.
ASPINA can offer solutions that are tailored to suit the functions and performance demanded by a diverse range of industries, applications, and customer products, as well as your particular production arrangements.
ASPINA supports not only customers who already know their requirements or specifications, but also those who are facing problems at early stages of development.
Do you struggle with the following concerns?
- Motor selection
-
- Don't have detailed specifications or design drawings yet, but need advice on motors?
- Don't have anyone in-house with expertise in motors and can't identify what sort of motor will work best for your new product?
- Motor and associated component development
-
- Want to focus your resources on core technology, and outsource drive systems and motor development?
- Want to save the time and effort of redesigning existing mechanical components when replacing your motor?
- Unique requirement
-
- Need a custom motor for your product, but been declined from your usual vendor?
- Can't find a motor that gives you the control you require, and about to give up hope?
Seeking answers to these problems? Contact ASPINA, we’re here to help.
List of the same series columns
- NEMA stepper motor sizes chart and selection guide
- What does a stepper motor do?
- What is a brushless DC motor? What is the difference between brushless motor and brushed motor?
- What is a DC motor? - DC motor types, how they work, and how to control them
- Applications for blower motor
- What is a blower motor?
- Features and applications of DC motors
- Advantages of brushless DC motors over brushed DC motors
- Is this brushless motor cheap or expensive? - What factors determine its price?
- What is a geared brushless DC motor?
- How does an electronic speed controller for a brushless DC motor work? And what should you consider when you choose the right one?
- Small brushless motors
- What are the disadvantages of brushless DC motors? And how can they be overcome?
- What is an actuator?
- Do brushless DC motors require a drive circuit? – Controlling brushless DC motors
- What is a stepper motor?
- What is an electric motor?
- How are stepper motors controlled? - Speed control of stepper motors
- How are DC motors controlled? - Speed control of DC motors
- Brushless DC motor applications: examples that demonstrate their features
- Stepper motor applications: Examples that demonstrate their features
- Motors designed for easy control: How do stepper motors work?
- What are the differences between brushed and brushless DC motors?
- What is a PSC motor
- What is a servo motor?
- What is a blower?
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others