Automotive HVAC
-
Automotive
-
Automotive HVAC system

3 Jul. 2023
Automotive HVAC is the air conditioning system installed in automobiles, such as passenger cars, pickup trucks, and heavy-duty trucks. Like other air conditioning systems, automotive HVAC cools air during the process of transforming refrigerant into a liquid or gas. The heating process on the other hand is characteristic to automotive HVAC as it uses the heat created by the engine.
In this article we describe what automotive HVAC are and how they work. We will also introduce some details of one of its main components, the blower.
What is automotive HVAC?
HVAC, which stands for Heating, Ventilation and Air Conditioning, is an air conditioning system that controls temperature, humidity, airflow, and air purity to maintain good indoor air quality at homes, offices, or cars.
Automotive HVAC is the air conditioning system installed in automobiles which has become one of the key elements in the automobile industry, in view of higher temperature control needs due to recent climate changes, higher consumer interest in air purification, and higher efficiency requirements fueled by the growing promotion of electric vehicles.
How do automotive HVAC work?
Automotive HVAC consists of the following main components:
- Compressor (The compressing refrigerant)
- Condenser (Cools refrigerant)
- Receiver dryer (Removes impurities and moisture from refrigerant)
- Expansion valve
- Evaporator (Cools air)
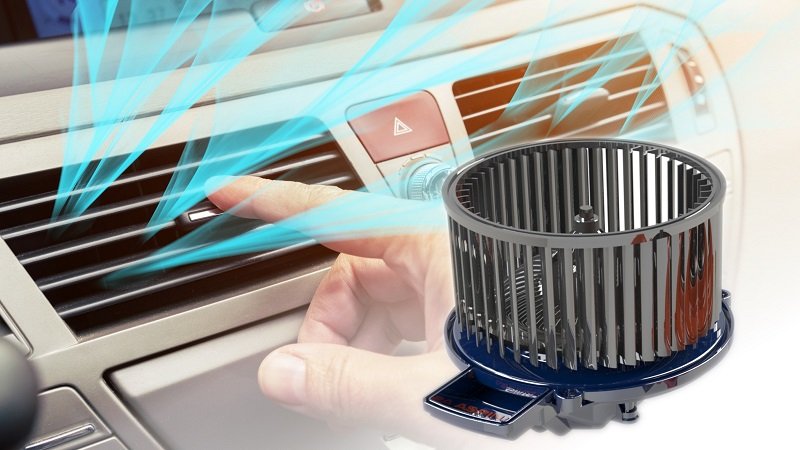
- Blower (Sends out air)
- Thermostat (Regulates temperature)
- Actuator (Switches air direction)
Like other air conditioning systems, automotive cooling systems cool air by transforming refrigerant into a liquid or gas, absorbing heat in the process.
First, the compressor compresses the refrigerant gas to a high-temperature, high-pressure state. This compressed refrigerant flows into the condenser and is cooled by outside air, turning into a liquid. After this cooled liquid refrigerant flows into the receiver dryer, and impurities and moisture are removed, it flows into the expansion valve. When the refrigerant is injected from the expansion valve, it is atomized and flows into the evaporator. The atomized refrigerant then evaporates and cools the evaporator, which absorbs heat from the air inside the car. Finally, this cooled air is blown back into the car by the blower.
Heating in automobiles, on the other hand, uses heat generated from the engine. Wind is applied to the heated engine coolant to create warm air, and a blower blows the warm air back into the car.
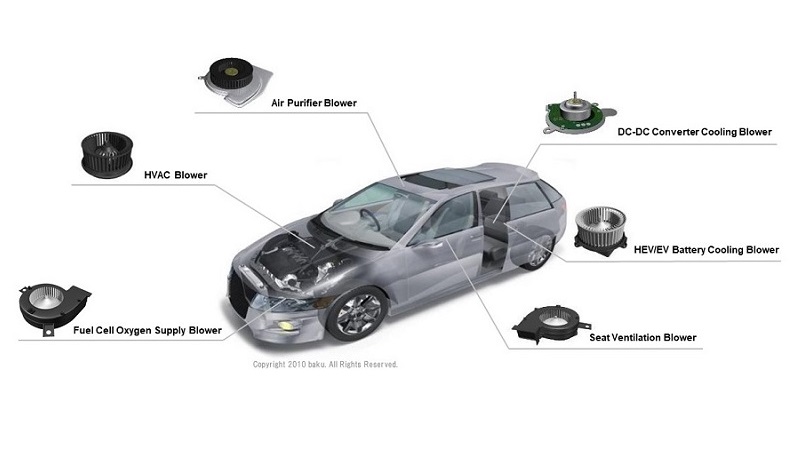
Automotive HVAC blowers
As mentioned above, automotive HVAC consists of several components, and the blower is one of them. The blower is one of the main components of automotive HVAC and is essential for sending out the heated or cooled air to its intended space. The following chapters will focus on automotive HVAC blowers.
In general, blowers, fans, and compressors are classified into four types: axial, diagonal, centrifugal (radial), and cross flow. Automotive HVAC blowers are classified as a multi blade centrifugal type.
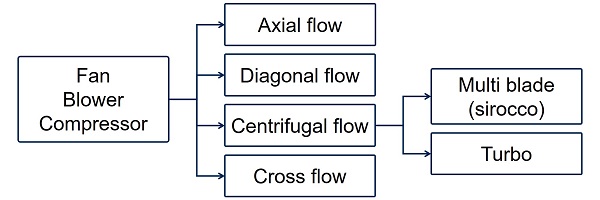
Centrifugal flow
Centrifugal flow blowers use the centrifugal power supplied from the rotation of impellers to increase the kinetic energy of air. When the impellers rotate, the air near the impellers are thrown off into the casing. As a result, the kinetic energy of air is measured as pressure because of the resistance offered by the casing and duct. The air is then guided to exit via outlet ducts.
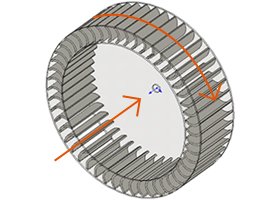
Multi blade (sirocco) type
The air flow in a multi blade (sirocco) type blowers is perpendicular to the axis of rotation, and the blades are typically angled forward in the direction of rotation. These types are often categorized as a mid-range in terms of flow rate and pressure, and are used in applications such as duct ventilation, air conditioning and cooling.
For more information on blower motors, click the link below:
Types of automotive HVAC blower
Automotive HVAC blowers are divided into two categories depending on whether it uses brushes and commutators in its DC motor. DC motors that use brushes and commutators are called brushed DC motors, while those that use an electronic circuit instead are called brushless DC (BLDC) motors. Due to the latest trends such as the shift to electric vehicles and higher interest toward sustainability, more manufacturers are choosing brushless DC motors to benefit from their compact, light, and quiet features.
For more information on HVAC blower motors, click the link below:
ASPINA’s automotive HVAC blowers
ASPINA has always found value in the performance of brushless DC motors and has been supplying automotive HVAC blowers using brushless DC motors to some of the largest Tier-1 companies in the world for over 20 years.
Benefits of ASPINA’s automotive HVAC blowers
- Long life
- Low noise
- Low electromagnetic noise
- Potential for energy saving
- Light weight
- EMC (Electro Magnetic Compatibility) strength
Produced on automated production line systems in our China and Mexico plants, our automotive HVAC blowers are highly rated by customers for their quietness and EMC strength. They are compact, and among the lightest blower motors in the industry, weighting only about 850g without the fan. They can also be customized and supplied either with or without fan to meet the precise need of HVAC manufacturers.
Overcome your problems with ASPINA’s HVAC blowers
The key to blower development is to study the electric motor, fan, impeller, circuitry, and other components in detail to build up an accurate understanding of where performances losses occur. ASPINA draws on their expertise built up through many years of development, not only to optimize blowers or their motors to improve their performance, but also to make them smaller, lighter, and more durable.
If you have any questions or would like samples, quotation, or detailed customization, please feel free to contact us from our form.
Contact us for more information
- New inquiry
- Prototype
- Upgrade
- Customization
- Your spec
- Literature
- Support
- Others